The Benefits of a Dual-Purpose Ultrasound System for Vascular Access and Bladder Scanning
Efficiency and accuracy are central to modern nursing practice, and fundamental bedside procedures such as vascular access and bladder assessment can have improved outcomes when performed swiftly. Bladder scanners are a vital device for obtaining precision bladder volume and enhancing the quality of care.
Historically, nurses have used completely separate devices for vascular access and bladder scanning, which can be cumbersome and time-consuming. Fortunately, ultrasound technology has progressed to the point where a single system is now available that does both jobs (and does them well). In this article, we discuss the benefits of combining them by using the Kosmos Platform for both vascular access and bladder scanning purposes, ultimately leading to improved workflow and better patient outcomes in a clinical setting.
Table of contents
- The Benefits of a Dual-Purpose Ultrasound System for Vascular Access and Bladder Scanning
Understanding the role of ultrasound in Nursing
As a non-invasive imaging technique, ultrasound plays an important role in nursing, as it offers improved diagnosis, treatment, and bedside procedures. Real-time imaging can help to enhance accuracy, efficiency, and outcomes for patients, especially in critical care, emergency, and post-operative settings [1].
Among professionals in the field of nursing practice, ultrasound is used to assist with the placement of peripheral intravenous catheters and measuring the volume of the bladder in patients suspected of having urinary retention. This avoids unnecessary catheterizations, increasing comfort and efficiency in the diagnostic process [2,3]. Ultrasound is accurate for vascular access and bladder assessments, and this prevents errors, complications, and erroneous diagnoses, leading to an enhanced patient experience [4,5].
The importance of bladder scanning in Nursing
A bladder scan is a non-invasive ultrasound method used to measure bladder volume and identify urinary retention. It is an important factor in diagnosing urinary retention, facilitating catheterization decisions, and monitoring postoperative patients [6].
According to some studies, bladder scanning is important for preventing post-operative urinary retention (POUR), improving discharge efficiency, and decreasing the length of stay in the hospital. The exact measurement of bladder volume obtained with bladder scanning minimizes unnecessary catheterizations and the risk of catheter-associated urinary tract infections [6,7]. Proper skills in using bladder scanners allow improved clinical results and nursing care [8].
The role of ultrasound in Vascular Access
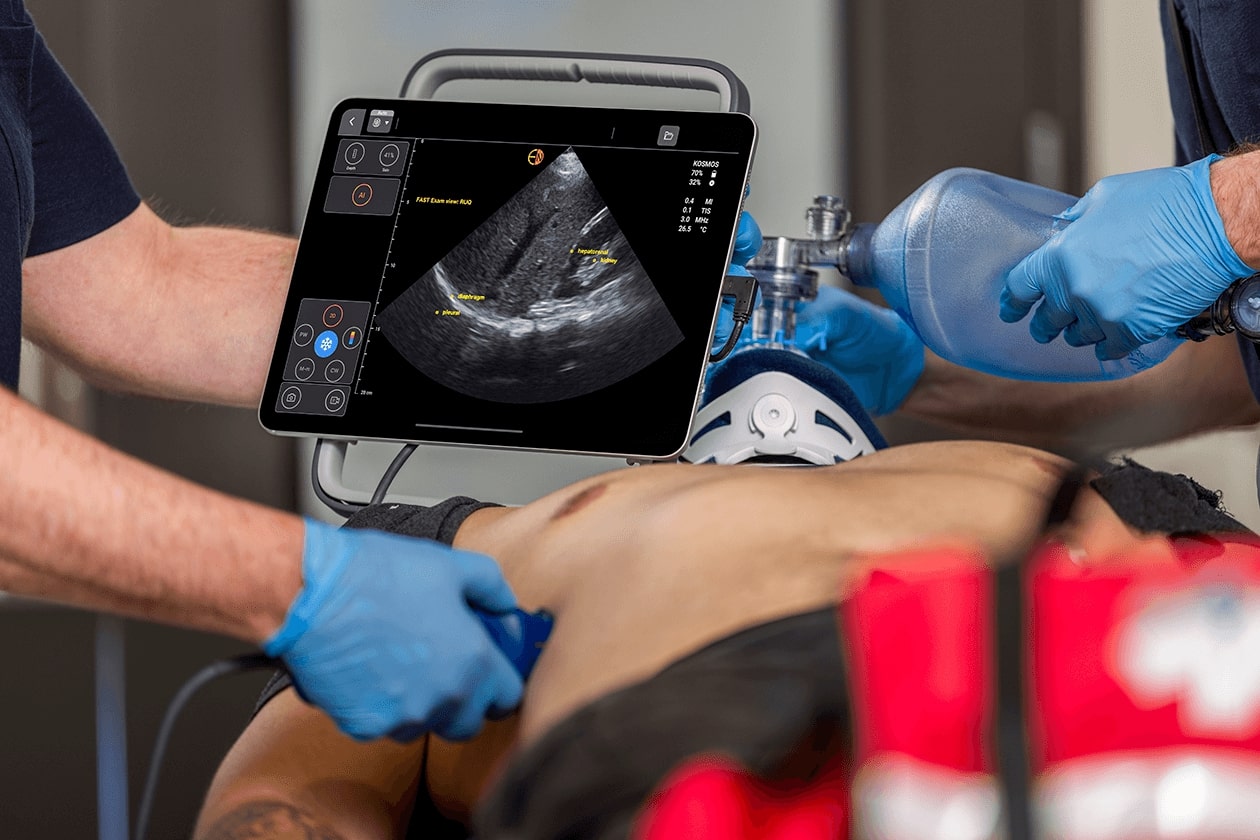
The importance of vascular access in drug transportation, fluid administration, and hemodynamic monitoring remains paramount in the acute care environment where time and precision are critical [9]. Conventional techniques use anatomical bony landmarks and palpation, which may be hard in patients with problematic veins. These methods potentially result in multiple attempts with the needle, which can lead to complications like vascular puncture, hematoma, and infiltration [10,11]. Using ultrasound guidance, nurses can visualize veins better, help select appropriate puncture sites, and assess vein patency in real time [12]. It also allows for clear visualization of the needle tip throughout the process, which improves first-pass success rates and decreases complications [13]. The use of ultrasound technology in vascular access procedures can improve accuracy, increase patient safety, and lessen the risks associated with traditional techniques [14].
Why Combine Vascular Access and Bladder Scanning in one System?
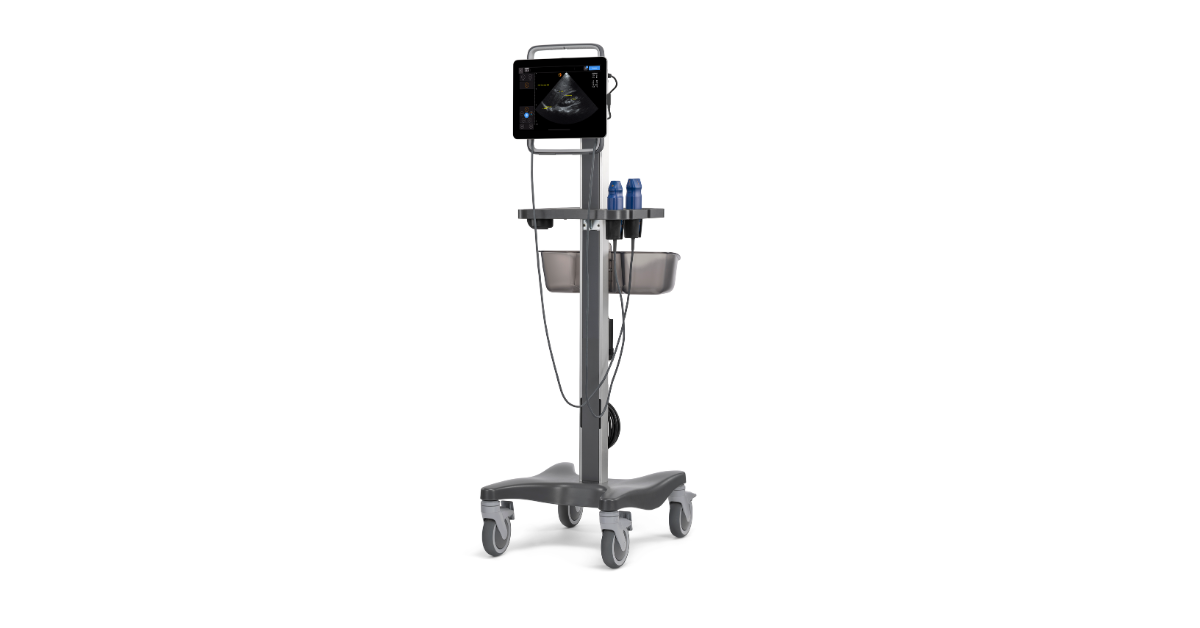
Vascular access and bladder scanning functionalities combined in a single ultrasound system are advantageous for nursing practice. By combining the two abilities, nurses can streamline the workflow, make the patient more comfortable, and save costs, thereby ultimately improving the quality of care.
Enhanced Efficiency in Nursing Workflow
A dual-purpose system enables nurses to cycle through vascular access and bladder scanning without needing to change out the device. This integration prevents delays, making bedside care tasks more streamlined and efficient with better time management, given the possibility of tight clinical schedules [12].
Improved Patient Comfort and Safety
One system minimizes the need for frequent repositioning, which improves the comfort of the patients, especially those with mobility issues. Reducing position changes reduces errors in the process as well, enhancing safety as well as outcomes.
Cost-Effectiveness and Resource Management
A combination probe minimizes the requirements for multiple devices, reducing equipment expenses and streamlining upkeep. Decreases training time, as staff can become familiar with one device platform.
This optimization of nursing care workflow, patient experience, and resource management is accomplished through an integrated approach.
Best Practices for Implementing a Dual-Purpose Ultrasound System
Incorporating dual-purpose ultrasound systems into clinical practices should include practice-oriented training, maintenance, and documentation appropriate for health professionals. Nurses should be systematically trained to master vascular access and bladder scanning techniques so they can be confident in successfully operating devices and interpreting images.
Image quality and device performance can be achieved through regular servicing, calibration & remedial action. Calibration procedures, like phantom-based experiments, can improve probe accuracy and mitigate errors. Finally, detailed clinical record documentation is of utmost importance for keeping a log of all assessments performed, facilitating communication, and ensuring the quality of patient care.
Revolutionize your nursing practice with a dual-purpose ultrasound system, combining efficiency and precision. Integrating vascular access with bladder scanning in a single ultrasound device can help you streamline workflows and enhance patient comfort and care quality.
Go further with your clinical practice — Discover what this innovative solution can do for you!
Conclusion
A dual-purpose ultrasound system helps improve workflow efficiency, patient safety, and cost savings. Integrating vascular access and bladder scanning capabilities allows nurses to reduce equipment clutter, decrease patient discomfort, and increase procedural accuracy. This technology empowers nurses to implement multiple assessments without disrupting care by switching devices. By adopting this innovative solution in their practice, nurses can use its advantages to provide better, wiser, and safer healthcare in order to advance patient outcomes and improve clinical efficiency.
References
1. Sozzi, M., et al. (2019). Ultrasound-Guided Nursing. In A. Sarti & F. L. Lorini (Eds.), Textbook of Echocardiography for Intensivists and Emergency Physicians (pp. 403–411). Springer International Publishing.
2. Morata, L., et al. (2020). Ultrasound-Guided Peripheral Intravenous Catheter Insertion: The Nurse’s Manual. Critical Care Nurse, 40(5), 38–46.
3. Rabito, L., et al. (2023). Point-of-care ultrasound praxis at the bedroom by resident nurses in the bladder residual assessment. JBMEDE – Jornal Brasileiro de Medicina de Emergência, 3, e23004.
4. Steinwandel, U., et al. (2017). Use of ultrasound by registered nurses-a systematic literature review. Journal of Renal Care, 43(3), 132–142.
5. Colombo, A., et al (2020). Urinary Bladder Test Device to Integrate Basic Ultrasound Training for Nurses. Ultrasound in Medicine & Biology, 46(10), 2855–2860.
6. Palese, A., et al. (2010). The effectiveness of the ultrasound bladder scanner in reducing urinary tract infections: A meta-analysis. Journal of Clinical Nursing, 19(21–22), 2970–2979.
7. Schallom, M., et al. (2020). Accuracy of Measuring Bladder Volumes With Ultrasound and Bladder Scanning. American Journal of Critical Care: An Official Publication, American Association of Critical-Care Nurses, 29(6), 458–467.
8. Liptrott, S. J., et al. (2024). Nurse performed bladder ultrasound: A clinical quality improvement initiative. Contemporary Nurse, 1–17.
9. Schmidt, G. A., et al. (2019). Ultrasound-guided vascular access in critical illness. Intensive Care Medicine, 45(4), 434–446.
10. Maecken, T., & Grau, T. (2007). Ultrasound imaging in vascular access. Critical Care Medicine, 35(5 Suppl), S178-185.
11. Franco-Sadud, R., et al. (2019). Recommendations on the Use of Ultrasound Guidance for Central and Peripheral Vascular Access in Adults: A Position Statement of the Society of Hospital Medicine. Journal of Hospital Medicine, 14(9), E1–E22.
12. Saugel, B., et al. (2017). Ultrasound-guided central venous catheter placement: A structured review and recommendations for clinical practice. Critical Care (London, England), 21(1), 225.
13. Seto, A. H., et al. (2010). Real-Time Ultrasound Guidance Facilitates Femoral Arterial Access and Reduces Vascular Complications: FAUST (Femoral Arterial Access With Ultrasound Trial). JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, 3(7), 751–758.
14. Leibowitz, A., et al. (2020). Ultrasound Guidance for Central Venous Access: Current Evidence and Clinical Recommendations. Journal of Intensive Care Medicine, 35(3), 303–321.
15. Andersen, C. A., et al. (2019). Point-of-Care Ultrasound in General Practice: A Systematic Review. The Annals of Family Medicine, 17(1), 61–69.