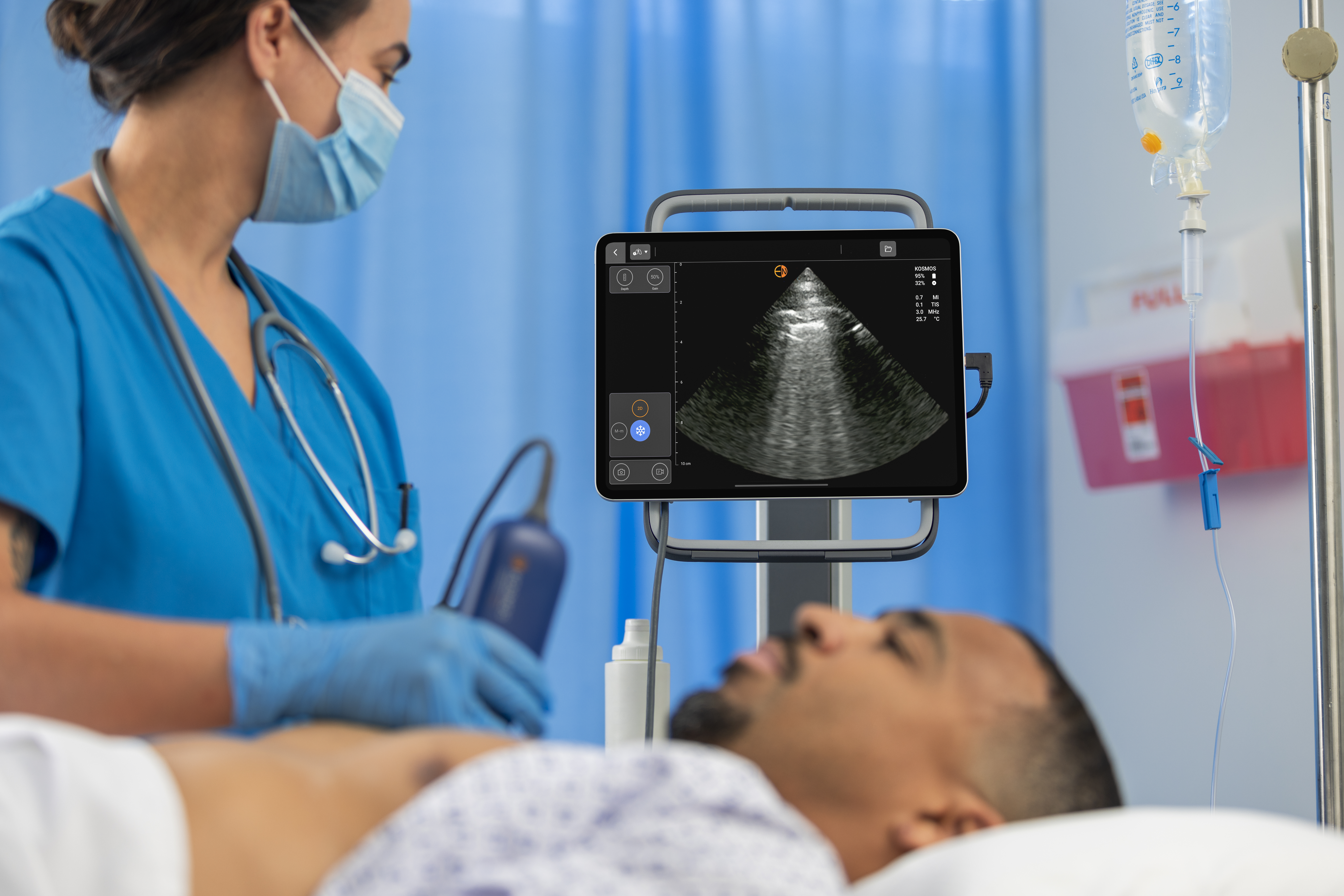
What Role Does Ultrasound Play in Sepsis?
Table of contents
Sepsis is one of the leading causes of critical illnesses and high mortality rates in ICU and emergency departments. Early, accurate diagnosis is essential. While laboratory investigations and clinical evaluations are vital, ultrasound has transformed sepsis management since it provides real-time insights which can enhance treatment decisions significantly.
Point-of-care ultrasound (POCUS) can provide clinicians crucial benefits with septic patients like securing vascular access, evaluating cardiac functions, and diagnosing complications such as septic arthritis.
Clinicians using POCUS can get rapid, detailed assessments across different body organs and systems including cardiac and respiratory evaluations, and pinpointing infection sources.
Evaluation of Respiratory Failure in Septic Patients
Respiratory failure is one of the most common complications in septic patients, which either originates from cardiac or pulmonary origins. In these cases, lung ultrasound is usually the first diagnostic line because it offers a quick evaluation and differentiation between cardiac and non-cardiac causes of hypoxia and dyspnea.
Identification of Pulmonary Edema with B-lines
B-lines are the best characteristic of pulmonary edema, resulting from cardiac and non-cardiac causes. They are caused by interstitial edema, increased fluid, or fibrosis in the interlobular septae. The origin of edema is crucial for its management, especially in making precise decisions on vasopressors and fluids.
Pneumothorax, Pneumonia, and Pleural Effusion
Lung Ultrasound is also a rapid, effective tool for diagnosing pneumothorax, pneumonia, and pleural effusion. All these can contribute to circulatory and respiratory failure in septic patients. Early identification of these problems makes the management much faster.
Echocardiography in Bilateral B-Lines
Focused echocardiography should be performed when bilateral B-lines are seen since it helps determine if the pulmonary edema is cardiac or not, which can affect the vasopressor and fluid management (1).
Explore how EchoNous’ ultrasound solutions improve outcomes for critical care patients with real-time, bedside imaging.
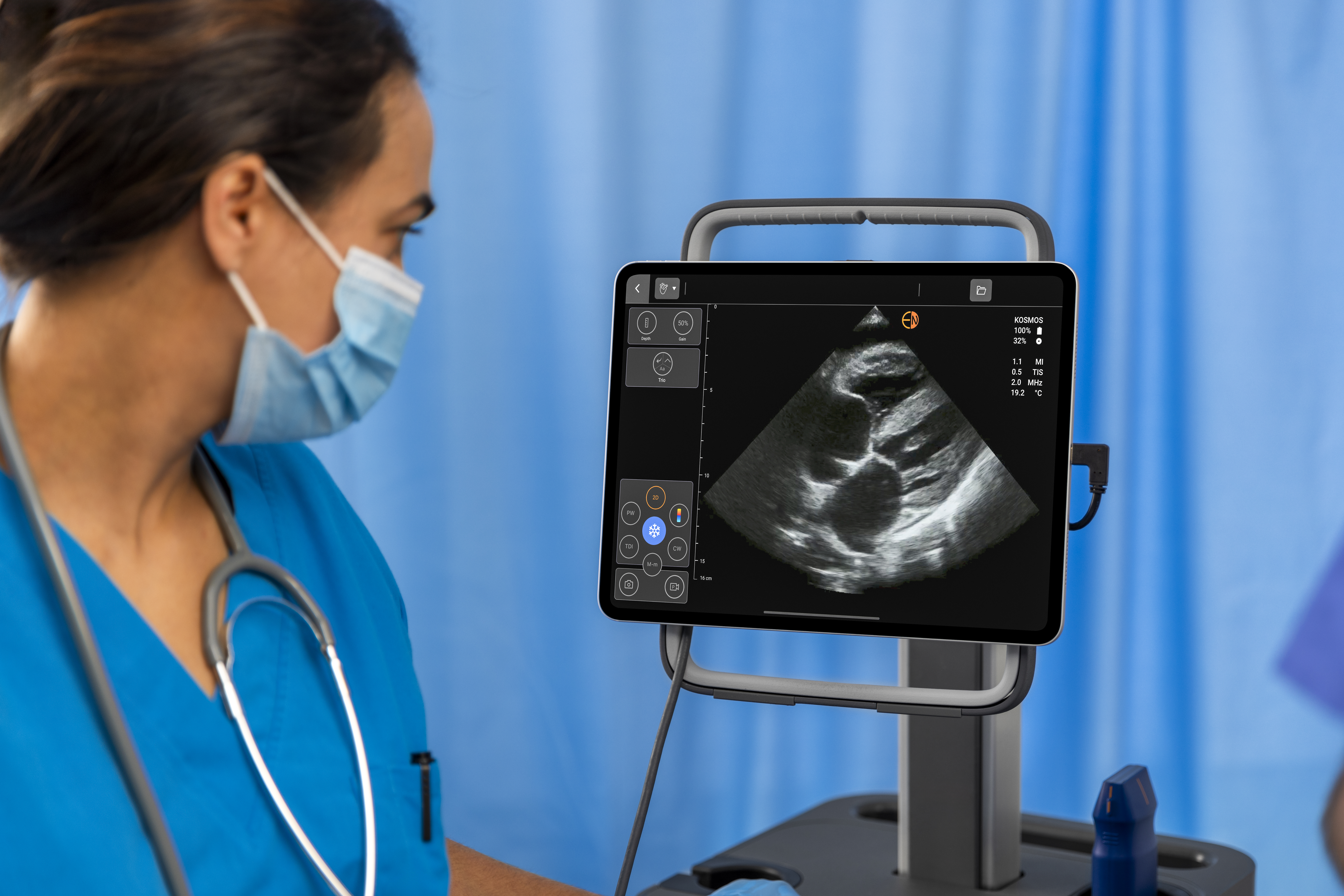
Vascular Access in Septic Patients
Septic patients usually suffer from hypotension, dehydration, and maybe other underlying medical conditions, which can make their venous access very difficult.
This is where ultrasound-guided vascular access helps. It can help in improving the success rate and cannulation speed, which means faster administration of fluids and medications.
Central Venous Access
Ultrasound-guided central venous catheterization is useful in the management of septic patients since it minimizes the risk of complications including arterial injuries and allows clinicians to visualize the catheter placement to make sure it is in the right place (2).
Peripheral IV Access
If the patient does not need central venous access but his or her veins are difficult, ultrasound-guided peripheral IV (PIV) access is a great option. Studies show that ultrasound-guided vascular access decreases the cannulation time by more than 30%, which makes the intervention much faster (3).
Elevate your vascular access capabilities with the Kosmos Vascular Access Bundle
Vasopressor Selection and Initiation in Septic Shock
Septic shock needs vasopressors in most cases to maintain hemodynamic stability. The selection of the most effective vasopressor and when to start it can be challenging. That is why cardiac ultrasound can provide insights into cardiac functions and guide clinicians on the use of vasopressors.
Differentiating Cardiogenic and Hypovolemic Shock
Focused echocardiography can help differentiate distributive and cardiogenic shocks. A hypodynamic heart indicates cardiogenic shock, which requires inotropic support. On the other hand, a hyperdynamic heart with low filling pressures is suggestive of distributive shock, which usually requires norepinephrine (4).
Left Ventricular Outflow Tract (LVOT) Velocity-Time Integral (VTI)
LVOT VTI helps determine cardiac output and stroke volume. This will further determine fluid resuscitation and vasopressor therapy. Ultrasound assessment of LVOT VTI helps clinicians determine whether the septic patient needs more fluids or whether the vasopressors will be enough (5).
Cardiogenic Shock in Septic Patients
Echocardiography is one of the best tools to assess cardiogenic shock since it provides insights into cardiac function and structure.
Visualizing Cardiac Function
Echocardiography provides clinicians with direct visualization of the contraction and valve movement of the heart, which identifies cardiogenic shock from myocardial ischemia, acute valve diseases, aortic pathologies, and cardiomyopathy.
Sepsis-Induced Myocardial Dysfunction
In 60% of ICU patients, sepsis can induce myocardial dysfunction, which leads to cardiogenic shock. Even though this condition is hard to diagnose clinically, echocardiography can diagnose septic cardiomyopathy. This will help in medications with either inotropes or vasopressors. In septic patients, cardiac functions can vary on a daily basis. Therefore, re-evaluation with ultrasound is crucial for effective and timely adjustment in management (6).
Learn more about the advanced cardiac capabilities on the Kosmos Torso-One probe.

Septic Arthritis and Joint Effusions
Sepsis can be caused by joint effusions and septic arthritis. The symptoms are usually joint swelling and effusion. Ultrasound is highly recommended for joint problems, especially when clinical examinations and other radiological assessments are inconclusive (7,8).
Differentiating Effusions from Haemarthrosis and Synovitis
Joint effusions can be difficult to differentiate from haemarthrosis or synovitis by clinical examination. Ultrasound can help in detecting the smallest volumes of fluid accurately. In septic effusions, the existence of proteinaceous fluid or cellular debris is conclusive.
Guiding Joint Aspiration in Suspected Septic Arthritis
Ultrasound is used in septic arthritis cases to perform ultrasound-guided joint aspiration. Clinicians use this technique to acquire a sample to analyze it in order to confirm or exclude septic arthritis and determine the best possible treatment approach.
Want to know more about Musculoskeletal ultrasound (MSK ultrasound)? We’ve got you covered.
Conclusion
Ultrasound has transformed sepsis management by providing rapid, precise, and non-invasive assessment for all patients, especially critical patients. From helping in vascular access, diagnosing respiratory failure, guiding vasopressor therapy, and assessing septic arthritis, ultrasound can significantly improve patient outcomes.
By adding the capabilities available on Kosmos to sepsis management, healthcare professionals are equipped with the latest in AI-driven ultrasound, enabling timely and precise bedside assessments that further enhance decision-making skills and improve patient outcomes.
Ready to take your patient care to the next level? Request a demo now and let’s talk!
References
- Lichtenstein D. A. (2014). Lung ultrasound in the critically ill. Annals of intensive care, 4(1), 1. https://doi.org/10.1186/2110-5820-4-1
- Randolph, A. G., Cook, D. J., Gonzales, C. A., & Pribble, C. G. (1996). Ultrasound guidance for placement of central venous catheters: a meta-analysis of the literature. Critical care medicine, 24(12), 2053–2058. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003246-199612000-00020
- Egan, G., Healy, D., O’Neill, H., Clarke-Moloney, M., Grace, P. A., & Walsh, S. R. (2013). Ultrasound guidance for difficult peripheral venous access: systematic review and meta-analysis. Emergency medicine journal : EMJ, 30(7), 521–526. https://doi.org/10.1136/emermed-2012-201652
- Pérez, C., Diaz-Caicedo, D., Almanza Hernández, D. F., Moreno-Araque, L., Yepes, A. F., & Carrizosa Gonzalez, J. A. (2024). Critical Care Ultrasound in Shock: A Comprehensive Review of Ultrasound Protocol for Hemodynamic Assessment in the Intensive Care Unit. Journal of clinical medicine, 13(18), 5344. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13185344
- Pérez-Manjarrez, A., García-Cruz, E., Gopar-Nieto, R., Jiménez-Rodríguez, G. M., Lazcano-Díaz, E., Rojas-Velasco, G., & Manzur-Sandoval, D. (2023). Usefulness of the velocity-time integral of the left ventricular outflow tract variability index to predict fluid responsiveness in patients undergoing cardiac surgery. Echo research and practice, 10(1), 9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s44156-023-00022-z
- Vallabhajosyula S, Ahmed AM, Sundaragiri PR. Role of echocardiography in sepsis and septic shock. Ann Transl Med. 2020 Mar;8(5):150. doi: 10.21037/atm.2020.01.116. PMID: 32309299; PMCID: PMC7154469.
- Meyer, R., Lin, C., Yenokyan, G., & Ellen, M. (2022). Diagnostic Utility of Ultrasound Versus Physical Examination in Assessing Knee Effusions: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Journal of ultrasound in medicine : official journal of the American Institute of Ultrasound in Medicine, 41(1), 17–31. https://doi.org/10.1002/jum.15676
- Zamzam M. M. (2006). The role of ultrasound in differentiating septic arthritis from transient synovitis of the hip in children. Journal of pediatric orthopedics. Part B, 15(6), 418–422. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.bpb.0000228388.32184.7f